Elbe basin: flood, low flow, hydrometeorological condition, water quality
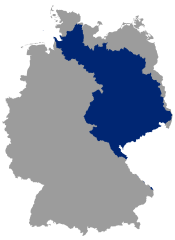
The River Elbe originates in the Giant Mountains (Czech Republic) and flows into the North Sea near Cuxhaven. Its total length is about 1100 km, of which around 730 km are located in Germany. Ten German federal states lie partially (Saxony, Thuringia, Saxony-Anhalt, Brandenburg, Lower Saxony, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Schleswig-Holstein, Bavaria) or completely (Berlin, Hamburg) in the catchment area of the Elbe.
The Elbstrom chainnage used for shipping and navigation on the Elbe inland waterway begins at the German / Czech border near Schöna (km 0.0) and ends at Cuxhaven-Kugelbake (sea border) (km 727.70). The Elbe / Labe chainage used in the Czech Republic has its zero position at Mělník (confluence of the Vltava).
The course of the River Elbe is divided into the sections "Upper Elbe" (source of the Elbe to Hirschstein Castle [near Meißen]), "Middle Elbe" (Hirschstein Castle to Geesthacht weir) and "Lower Elbe" (Geesthacht weir to the estuary mouth of the North Sea).
The entire catchment area of the Elbe has a size of about 150,000 sq. km, 65.5 % in Germany, 33.7 % in the Czech Republic, 0.6 % in Austria and 0.2 % in Poland. The main tributaries of the Elbe are the Vltava, the Eger (Ohře), the Schwarze Elster, the Mulde, the Saale and the Havel. [1]
The following international and national commissions / working groups advocate for water protection and flood risk management on the Elbe and its tributaries:
- ICPER - International Commission for the Protection of the Elbe River
- German - Czech Commission on Border Rivers
- FGG Elbe - River basin community Elbe
- AWE - Association of water suppliers in the Elbe basin
Elbe:
Selection of gauges / water quality monitoring stations
Elbe:
Current hydrometeorological conditions

Elbe:
Extreme floods / low flows

Elbe:
Current water temperature / oxygen content

Elbe:
Current electric conductivity / pH-value
Elbe:
Special monitoring program for hydrological extremes
Overview Elbe basin
- IKSE: Die Elbe
- IKSE (Hrsg.) (2005): Die Elbe und ihr Einzugsgebiet - Ein geographisch-hydrologischer und wasserwirtschaftlicher Überblick (PDF - 174 MB)
- Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit (Hrsg.) (2000 - 2003): Hydrologischer Atlas von Deutschland (HAD)
Water quality
- [1] IKSE (Hrsg.) (2022): Internationaler Bewirtschaftungsplan für die Flussgebietseinheit Elbe (Teil A)
- IKSE: Entwicklung der Gewässergüte der Elbe
- IKSE (Hrsg.) (2014): Sedimentmanagementkonzept der IKSE - Vorschläge für eine gute Sedimentmanagementpraxis im Elbegebiet zur Erreichung überregionaler Ziele (PDF - 33 MB)
- FGG Elbe (Hrsg.) (2021): Bewirtschaftungsplan nach § 83 WHG bzw. Artikel 13 der Richtlinie 2000/60/EG für den deutschen Teil der Flussgebietseinheit Elbe
- FGG Elbe (Hrsg.) (2007): Bericht der Flussgebietsgemeinschaft Elbe zum Überwachungsprogramm nach Artikel 8 EG-WRRL
- FGG Elbe (Hrsg.): Gewässergüte - Berichte / Zahlentafeln
- FGG Elbe (Hrsg.): Datenportal der FGG Elbe (historische und aktuelle Messdaten der Messprogramme, Visualisierung und Download)
- Institut für Hygiene und Umwelt [Hamburg]: Hamburger Wassergütemessnetz
- Landesamt für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Geologie [Mecklenburg-Vorpommern]: Gewässergüte im Kontext der EG-Wasserrahmenrichtlinie (WRRL)
- Landesbetrieb für Hochwasserschutz und Wasserwirtschaft Sachsen-Anhalt: Datenportal Gewässerkundlicher Landesdienst Sachsen-Anhalt
- Niedersächsischer Landesbetrieb für Wasserwirtschaft, Küsten- und Naturschutz: Landesdatenbank für wasserwirtschaftliche Daten
- Niedersächsischer Landesbetrieb für Wasserwirtschaft, Küsten- und Naturschutz: aktuelle Messwerte der Gütemessstationen
- Landesamt für Umwelt, Brandenburg: Messstationen des Wassergütemessnetzes - aktuelle Daten
- Landesamt für Umwelt, Brandenburg: Auskunftsplattform Wasser - Chemisch-physikalische Monitoringdaten
- Senatsverwaltung für Stadtentwicklung und Wohnen [Berlin]: Digitaler Umweltatlas Berlin (Gewässergüte [Chemie])
- Senatsverwaltung für Umwelt, Verkehr und Klimaschutz [Berlin]: Wasserportal Gewässerkundliche Messdaten
- Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie: Berichte und Bewertungen
- Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie: Aktuelle Gewässergütedaten (Messstationen) | Langzeitdaten (Messstationen)
- Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie: Gewässergütedaten: Datenportal iDA
- Thüringer Landesamt für Umwelt, Bergbau und Naturschutz: Gewässergüte (Qualität der Fließgewässer, Monitoringergebnisse, ...)
- Umweltbundesamt (Hrsg.) (2017a): Gewässer in Deutschland: Zustand und Bewertung
- Umweltbundesamt (Hrsg.) (2017b): Wasserwirtschaft in Deutschland - Grundlagen, Belastungen, Maßnahmen
- Umweltbundesamt (Hrsg.) (2022): Die Wasserrahmenrichtlinie - Gewässer in Deutschland 2021
- Umweltbundesamt (Hrsg.): Geographisches Informationssystem Umwelt
- European Environment Agency: Water quality monitoring stations (Karte der Messstellen der Wasserbeschaffenheit (Flüsse [und Kanäle], Seen [und Talsperren], Grundwasser, Übergangs-, Küsten- und Meeresgewässer) für die EU-Berichterstattung)
- European Environment Agency: Waterbase - Water Quality (Daten zur Wasserbeschaffenheit der Gewässer in Europa)
Accidental water pollution, warning and alarm plans
The Elbe / Labe in the Czech Republic
- Ministerstvo zemědělství (Landwirtschaftsministerium): Wasserwirtschaftliches Informationsportal (Überblick aktueller Zustand: Wasserstand und Durchfluss)
- Ceský hydrometeorologický ústav (Tschechisches Hydrometeorologisches Institut): Hochwasservorhersage; Hydrologische Situation im Überblick | Wasserstand / Durchfluss Elbegebiet
- Povodí Labe, státní podnik: Hydrologische Situation - Labe (Elbe)
- Povodí Vltavy, státní podnik: Hydrologische Situation - Vltava (Moldau)
- Povodí Ohře, státní podnik: Hydrologische Situation - Ohře (Eger)
Flood / low flow
- IKSE (Hrsg.) (2021): Internationaler Hochwasserrisikomanagementplan für die Flussgebietseinheit Elbe, Teil A
- IKSE (Hrsg.) (2012): Hydrologische Niedrigwasserkenngrößen der Elbe und bedeutender Nebenflüsse
- FGG Elbe (Hrsg.) (2021): Hochwasserrisikomanagementplan [...] für den deutschen Teil der Flussgebietseinheit Elbe, Teil A
- FGG Elbe: Hintergrunddokumente und -informationen der Länder und des Bundes zum Hochwasserrisikomanagement
- Niedersächsischer Landesbetrieb für Wasserwirtschaft, Küsten- und Naturschutz: Informationsportal Hochwasserschutz
- Landesamt für Umwelt, Brandenburg: Hochwasserschutz
- Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie: Hochwasserschutz
- Sächsisches Landesamt für Umwelt, Landwirtschaft und Geologie: Niedrigwasser
- Hochwasserpartnerschaft Elbe (HPE): Informationsportal HPE
- Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde: Hochwassergefahren und -risikokarten (für alle Bundesländer)
Research projects / programmes
- ElbeXtreme: Monitoring und Modellierung extremer Ereignisse im Elbe-Ästuar und der Deutschen Bucht; Koordinierung: GEOMAR Helmholtz-Zentrum für Ozeanforschung Kiel, Förderung: BMBF, Laufzeit 2024 - 2026
- ELSA: Förderprojekt Schadstoffsanierung Elbsedimente; Koordinierung: Behörde für Umwelt und Energie Hamburg (BUE), Laufzeit 2010 - 2021
- KLIWAS: Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf Wasserstraßen und Schifffahrt in Deutschland; Programmkoordinierung: BfG, Programmpartner DWD, BSH, BAW, BfG; Träger: BMVBS, Laufzeit 2009-2013
- GLOWA-Elbe: Wirkungen des globalen Wandels auf den Wasserkreislauf im Elbegebiet; Koordinierung: Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung (PIK), Förderung: BMBF, Laufzeit 2000 - 2011
- RIMAX: Risikomanagement extremer Hochwasserereignisse; Koordinierung: GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ), Förderung: BMBF, Laufzeit 2005 - 2010
- Gesamtkonzept Elbe, Koordinierung: Bundesministerium für Digitales und Verkehr, Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz, nukleare Sicherheit und Verbraucherschutz.
